Featured Research Projects
Discover our most impactful and innovative research initiatives currently transforming science
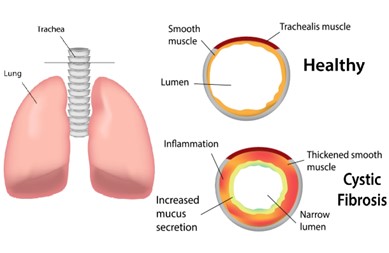
Analysis of Cystic Fibrosis Patients’ Condition using Multichannel Lung Sound Processing
Analysis of Cystic Fibrosis Patients’ Condition using Multichannel Lung Sound Processing
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs, digestive tract, and other areas of the body. It is one of the most common chronic lung diseases in children and young adults. It is a life-threatening disorder that should be diagnosed and controlled from childhood unless it can lead to death. That's why these patients should be monitored. There are three main tests to follow CF patients in consecutive visits: sputum culture test to detect infection, spirometry test to detect pulmonary function status, and CT to detect abnormalities in CF patients’ lungs. Sputum culture and pulmonary function tests are repeated every three months, and CT images are taken every three years. Because of exposure in taking a CT image, it cannot be used in shorter intervals. Therefore, irreversible disorders may be generated in shorter intervals. Physicians usually use lung auscultation as an essential primary diagnostic tool that has important information about lung conditions. The auscultation is subjective and cannot be heard from several areas at the same time. Lung auscultation has some advantages to other methods such as lack of radiation exposure, dynamic monitoring, and its low cost.

Automatic Depression Detection Based on Speech Processing and Artificial Intelligence
Automatic Depression Detection Based on Speech Processing and Artificial Intelligence
Psychological disorders, such as stress, anxiety, and depression, have been reported as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, which can result from the fear of death or illness, feeling helpless, social-distancing, working at home, and quarantine. Therefore, giving importance to monitoring and detecting depression is necessary. Although depression is prevalent, it is hard to detect due to its complicated and wide variety of symptoms, along with decreased in-person visits to a psychologist. As a result, speech processing, machine learning and artificial intelligence methods create special tools for early detection and facilitating depression monitoring.

Automatic Stuttering Detection from Reading Speech
Automatic Stuttering Detection from Reading Speech
More than 1% of the world's population suffers from stuttering. The speech therapist will start different treatments for each patient depending on the source of the stuttering, and during treatment, they should evaluate the success of their treatment by counting the number and types of speech dysfluencies. This counting is a time consuming process and is influenced by human error. To overcome this problem, by using speech processing techniques, automatic detection of speech dysfluencies can be implemented. Three common types of speech dysfluencies in stuttered speech are phoneme prolongation, syllable or word repetition, and blocking. Automatic diagnosis of speech dysfluencies saves time for speech therapists and increases the efficacy of speech therapy sessions. People with stuttering also have the opportunity to practice at home and self-assess, resulting in having fewer speech therapy sessions and saving time and money. In addition, the use of numerous and standard texts suggested for reading, increases the vocabulary size and confidence of subjects.
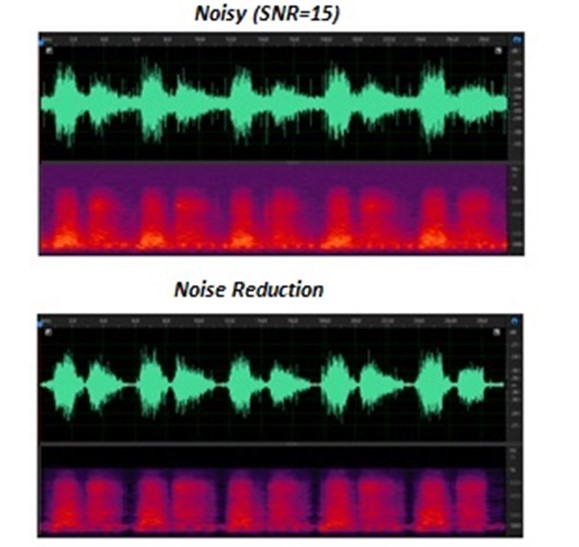
Denoising of Lung Sound Signals based on Combined EMD-ANN or DWT-ANN Models
Denoising of Lung Sound Signals based on Combined EMD-ANN or DWT-ANN Models
EMD: Empirical Mode Decomposition ANN: Artificial Neural Network DWT: Discrete Wavelet Transform Respiratory sounds are recorded in real-time in noisy environments. These signals are affected by various noises, including microphone contact, muscle contraction, and expansion, the noise of other medical devices, speech, mobile, etc. Different types of noise interfere with the recorded signals, resulting in misdiagnosis or non-diagnosis by the treating physician. Therefore, eliminating lung sound signal noise is very effective in diagnosing pulmonary disorders for prevention and treatment. However, noise removal is complicated due to its chaotic nature, non-static, and variable with the human body's physical state. One reason for the complexity of this task is the overlap of the primary signal spectrum and noise.
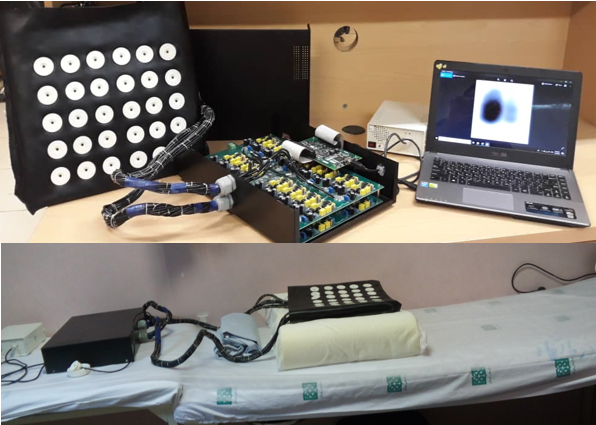

Design and Implementation of 30 channel Lung Sound Recording System
Design and Implementation of 30 channel Lung Sound Recording System
Lung disease is one of the high-risk diseases that decreases the patient's life. There are several devices and ways for diagnosing this disease, such as lung imaging and spirometry tests. One of the simplest and oldest ways is auscultation of lung sounds by stethoscope. Because of problems such as dependence on hearing of physician, inappropriate response frequency and the impossibility of record, store, and process of data, researchers turned to multichannel respiratory sound recording like acoustic imaging of lung sound features. The purpose is access to information of different pulmonary areas. Acoustic imaging of lung sound features in compare to other imaging methods like MRI and CT scan is completely non-invasive and don’t have problems, such as limitation in imaging time, high cost, and difficult access. In addition, the possibility of dynamic and online imaging of breathing process is one of the advantages of this method.
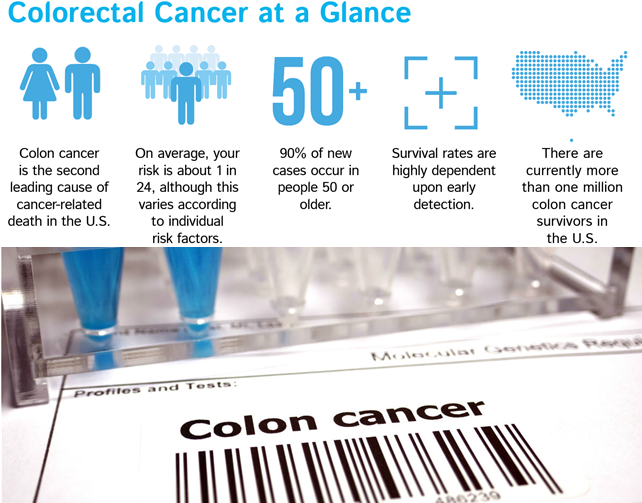
Predicting Colorectal Cancer Metastases from Registry Data
Predicting Colorectal Cancer Metastases from Registry Data
Colon cancer — also known as colorectal cancer — is the third most common type of cancer in the Iran, and the second most common cause of cancer deaths in people. From 135,000 new cancer patients in Iran, it has the third rank of occurrence by more than 12500 patients (about 9% of total cancer patients), and second in cancer deaths by 5000 deaths a year. A cancer registry is a collection of information about individuals, focused around the diagnosis and condition of cancer patients. Using cancer registry data can be useful to improve patients’ choices, help individuals reduce the risk of disease, and access the best care. It identifies and quantifies inequalities, improves the cost-effectiveness and quality of services and supports cancer research. Although there are numerous individual datasets containing important information about the disease and its management, we need to use our local datasets to have a better and more reliable outcome in our products. Nowadays, due to having enormous data of patients, models that can predict future incidence are evolving and providing us with better results. This encourages both scientists and physicians to rely on the outcomes, so prediction of disease is now a common research among researchers.